CRM System Pricing: 7 Shocking Truths You Must Know
Choosing the right CRM system pricing model can make or break your business growth. With so many options, hidden fees, and confusing tiers, it’s easy to overspend—or underinvest. Let’s cut through the noise and reveal what you’re really paying for.
Understanding CRM System Pricing: The Basics

Before diving into specific costs, it’s essential to understand what CRM system pricing actually entails. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are tools designed to help businesses manage interactions with current and potential customers. These platforms streamline sales, marketing, customer service, and analytics. But how much do they cost, and what factors influence the price? The answer isn’t straightforward, as CRM system pricing varies widely based on features, deployment models, and vendor policies.
What Is a CRM System?
A CRM system is software that collects customer data across multiple channels—email, phone, social media, and websites—and organizes it into a centralized database. This enables teams to track customer interactions, manage leads, automate workflows, and improve customer retention. From small startups to multinational corporations, businesses use CRM platforms to boost efficiency and drive revenue.
- Salesforce automation
- Marketing campaign management
- Customer support ticketing
- Analytics and reporting
Popular examples include Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM, and Microsoft Dynamics 365. Each offers different features and pricing structures, making it crucial to evaluate your needs before committing.
Why CRM System Pricing Matters
CRM system pricing directly impacts your return on investment (ROI). Overpaying for unnecessary features drains budgets, while underinvesting can limit scalability and functionality. According to Gartner, companies that implement CRM effectively see an average revenue increase of 41%. However, poor selection based on misleading pricing models can lead to abandonment or costly migrations later.
“The true cost of a CRM isn’t just the monthly fee—it’s the time, training, integration, and opportunity cost of choosing wrong.” — CRM Industry Analyst, 2023
Common CRM Deployment Models and Their Cost Implications
CRM systems come in three primary deployment models: cloud-based (SaaS), on-premise, and hybrid. Each has distinct CRM system pricing implications.
- Cloud-Based (SaaS): Most popular today, SaaS CRMs like HubSpot and Salesforce charge subscription fees per user per month. Initial costs are low, but long-term expenses can accumulate.
- On-Premise: Requires upfront licensing fees, server infrastructure, and IT staff. While more expensive initially, some enterprises prefer this for data control.
- Hybrid: Combines cloud and on-premise elements, offering flexibility but often increasing complexity and cost.
For most small to mid-sized businesses, cloud-based CRM system pricing is the most accessible and scalable option.
Key Factors That Influence CRM System Pricing
CRM system pricing isn’t one-size-fits-all. Multiple variables affect how much you’ll pay, from the number of users to advanced automation features. Understanding these factors helps you negotiate better deals and avoid surprise charges down the line.
Number of Users and Seat-Based Pricing
Most SaaS CRM platforms use a per-user, or seat-based, pricing model. You pay a fixed rate for each employee who accesses the system. For example, Salesforce Sales Cloud starts at $25/user/month, while HubSpot CRM offers a free tier and paid plans from $45/user/month.
While this seems simple, costs scale quickly. A team of 50 users on a $50/month plan spends $30,000 annually. Some vendors offer volume discounts, but these are often negotiable only for enterprise contracts.
- Free tiers usually limit user count or functionality
- Mid-tier plans charge $20–$70/user/month
- Enterprise plans may exceed $100/user/month
Tip: Consider whether every employee needs full access. Some vendors offer ‘light’ or ‘collaborator’ licenses at lower rates.
Feature Tiers and Module Add-Ons
Vendors segment their offerings into tiers—often labeled as ‘Starter,’ ‘Professional,’ ‘Enterprise,’ or similar. Each tier unlocks additional features, and upgrading isn’t always linear in cost.
For instance, Zoho CRM’s pricing jumps from $14/user/month (Standard) to $40/user/month (Enterprise), more than doubling for advanced AI and workflow automation. Similarly, Microsoft Dynamics 365 offers modular pricing, where sales, service, and marketing modules are sold separately.
- Basic tiers include contact management and lead tracking
- Mid-tier adds email marketing, automation, and reporting
- Premium tiers offer AI insights, telephony integration, and custom development
Be cautious of feature bloat. You may not need AI-powered forecasting if you’re a 10-person sales team.
Integration and API Access Costs
CRM systems rarely work in isolation. They must integrate with email platforms (Gmail, Outlook), marketing tools (Mailchimp, ActiveCampaign), e-commerce systems (Shopify, WooCommerce), and internal databases. While basic integrations are often free, advanced API usage or third-party connectors can incur extra fees.
Some platforms charge based on API call volume. For example, Salesforce imposes API limits per license type, and exceeding them requires purchasing additional API packs at $1,200/year for 1,000 extra calls.
“One client spent $8,000 in unplanned API fees after syncing their CRM with a custom ERP system.” — IT Consultant, TechAudit Group
Always review API policies and integration costs before signing a contract.
Hidden Costs in CRM System Pricing You Can’t Ignore
The advertised price is rarely the full story. Hidden costs in CRM system pricing can add 20–50% to your total cost of ownership (TCO) over three years. These include implementation, training, customization, and renewal fees.
Implementation and Setup Fees
While SaaS CRMs promise quick setup, complex deployments require professional services. Vendors like Salesforce and Microsoft often charge $5,000–$25,000 for initial configuration, data migration, and workflow design.
Some companies opt for third-party consultants, which can cost $150–$300/hour. Even ‘self-serve’ platforms like HubSpot may require weeks of internal effort to configure properly—time that translates to labor costs.
- Data migration from legacy systems
- Custom field and pipeline setup
- Role-based access configuration
Pro tip: Ask vendors if they offer free onboarding support or credits for implementation partners.
Training and Adoption Costs
A CRM is only as good as its adoption rate. If your team doesn’t use it, you’ve wasted money. Training is critical, yet often overlooked in CRM system pricing discussions.
Internal training sessions, external workshops, and ongoing support consume time and resources. According to Nucleus Research, companies spend an average of $2,500 per user on training and change management during CRM rollout.
- Online courses and certification programs
- Internal super-users or CRM champions
- Ongoing refresher sessions
Platforms with intuitive interfaces (e.g., HubSpot, Zoho) reduce training time, while complex systems like SAP CRM demand extensive onboarding.
Customization and Development Fees
Off-the-shelf CRM features rarely fit every business perfectly. Customization—such as building unique dashboards, automating niche workflows, or creating branded portals—requires development work.
Custom coding, third-party app development, or using low-code platforms within the CRM (like Salesforce Lightning) can add thousands to your budget. Salesforce partners often charge $10,000+ for custom app development.
“We built a custom quote generator in our CRM that saved 15 hours a week—but it cost $12,000 to develop.” — Operations Manager, B2B SaaS Company
Ask your vendor about built-in customization tools to reduce dependency on developers.
Top CRM Platforms and Their Pricing Breakdown
To make informed decisions, let’s compare the CRM system pricing of leading platforms. This section breaks down costs, features, and value propositions to help you identify the best fit for your budget and needs.
Salesforce: The Enterprise Leader
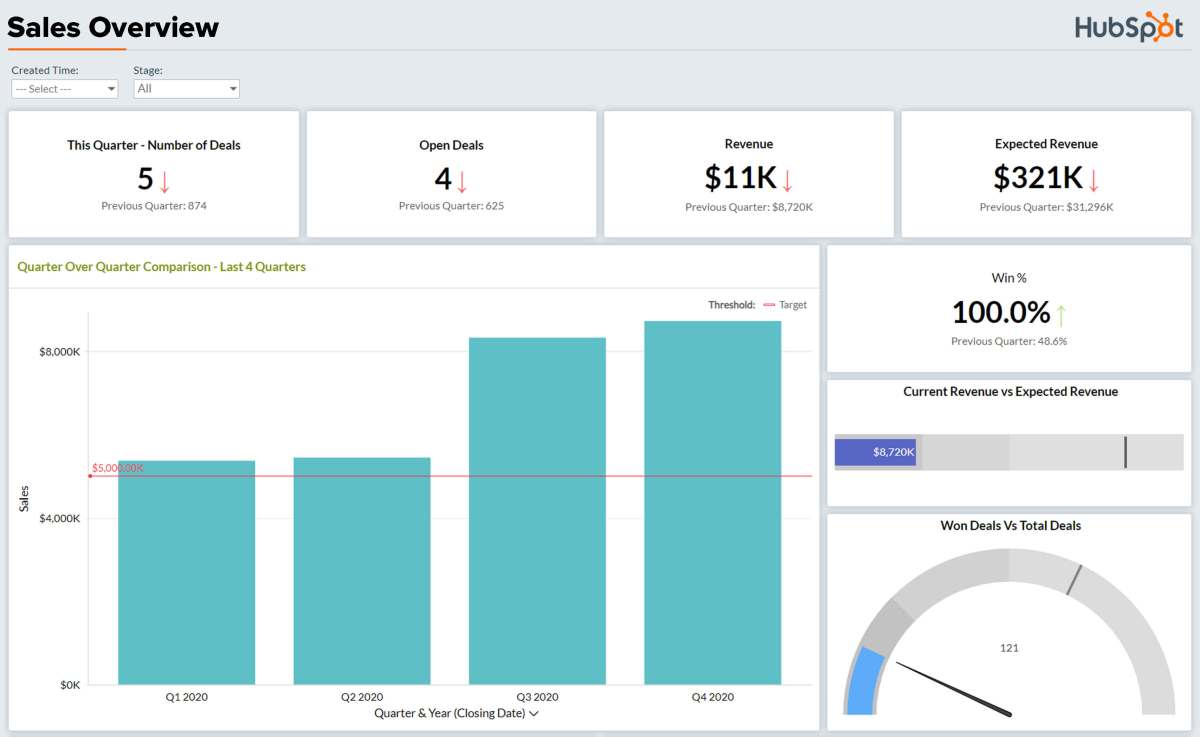
Salesforce dominates the CRM market with a 19.8% share (Statista, 2023). Its CRM system pricing is complex, segmented into multiple clouds and editions.
- Sales Cloud: $25–$300/user/month
- Service Cloud: $25–$165/user/month
- Marketing Cloud: Starts at $400/month (not per user)
The Essentials plan ($25/user) is basic, while Unlimited ($300/user) includes 24/7 support, unlimited custom apps, and advanced security. Add-ons like Einstein AI or CPQ (Configure, Price, Quote) can double costs.
Best for: Large enterprises needing scalability and deep customization.
HubSpot: The All-in-One Growth Platform
HubSpot stands out with a free CRM tier and seamless integration across sales, marketing, service, and CMS. Its CRM system pricing is transparent and user-friendly.
- Free CRM: $0, includes contact management, email tracking, and basic automation
- Starter: $45/month (not per user)
- Professional: $450–$1,200/month (based on contacts)
- Enterprise: $1,200+/month
Unlike most competitors, HubSpot’s Professional and Enterprise plans are billed per contact count, not per user—ideal for teams with many collaborators.
Best for: SMBs and marketing-driven organizations.
Zoho CRM: The Budget-Friendly Powerhouse
Zoho CRM offers exceptional value, especially for small businesses. Its CRM system pricing starts as low as $14/user/month, with robust features even in lower tiers.
- Standard: $14/user/month
- Professional: $23/user/month
- Enterprise: $40/user/month
- Ultimate: $52/user/month
Zia, Zoho’s AI assistant, is included in higher tiers, offering predictive lead scoring and sentiment analysis. Zoho also provides free migration from other CRMs.
Best for: Cost-conscious businesses needing AI and automation without enterprise price tags.
How to Choose the Right CRM System Pricing Model
Selecting the right CRM isn’t just about the lowest price—it’s about long-term value. The ideal CRM system pricing model aligns with your business size, growth trajectory, and operational needs.
Assess Your Business Size and Needs
Start by evaluating your team size, sales process complexity, and customer volume. A 5-person startup doesn’t need Salesforce Enterprise, just as a global retailer can’t rely on a free CRM forever.
- Small businesses (1–10 users): Prioritize ease of use and low entry cost. Consider HubSpot Free or Zoho Standard.
- Mid-sized companies (11–100 users): Look for automation, reporting, and integration capabilities. Salesforce Professional or HubSpot Professional may fit.
- Enterprises (100+ users): Focus on scalability, security, and customization. Salesforce Unlimited or Microsoft Dynamics 365 are strong contenders.
Map your customer journey and identify pain points a CRM can solve—this prevents overbuying.
CRM system pricing – CRM system pricing menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Compare Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Don’t just compare monthly fees. Calculate the total cost of ownership over 3–5 years, including:
- Subscription fees
- Implementation and setup
- Training and support
- Integration and API costs
- Renewal price increases (common with SaaS)
For example, a $30/user/month CRM for 20 users costs $7,200/year in subscriptions. Add $5,000 implementation and $10,000 training, and the first-year TCO hits $22,200.
“We saved 30% by switching from Salesforce to Zoho—without losing critical features.” — CFO, Mid-Market Tech Firm
Negotiate and Leverage Free Trials
Never accept the listed price without negotiation. Vendors often offer discounts for annual payments, multi-year contracts, or bundled modules.
- Ask for a 10–20% discount for paying annually
- Request free training or implementation credits
- Use free trials (14–30 days) to test performance
HubSpot, Zoho, and Salesforce all offer free trials. Use this time to simulate real workflows and measure user adoption.
Free vs. Paid CRM: Is Free Really Better?
Many vendors offer free CRM versions, but are they worth it? Let’s examine the trade-offs between free and paid CRM system pricing models.
Pros and Cons of Free CRM Systems
Free CRMs like HubSpot Free, Zoho CRM Free, and Freshsales Free provide basic functionality at zero cost—ideal for startups and solopreneurs.
- Pros: No financial risk, easy to start, good for learning
- Cons: Limited features, user caps, minimal support, branding in emails
HubSpot Free, for example, allows unlimited users but restricts email sending to 100 emails/month and lacks advanced reporting.
Free CRMs are great for testing, but rarely sufficient for growing businesses.
When to Upgrade to a Paid Plan
Consider upgrading when you hit any of these thresholds:
- More than 1,000 contacts
- Need for automation (e.g., email sequences, task assignments)
- Requirement for phone support or SLAs
- Desire for custom reporting or dashboards
- Integration with paid tools (e.g., Zoom, Slack, Shopify)
Upgrading too late can hurt productivity; upgrading too early wastes money. Monitor usage metrics to time your move.
Hidden Limitations of Free CRMs
Free CRMs often have hidden limitations that push you toward paid plans:
- Rate limits on email or API calls
- Watermarked communications
- No access to mobile apps or offline mode
- Delayed feature updates
Some free plans also restrict data export, making migration difficult later.
“We were locked in because our free CRM wouldn’t let us export call logs—cost us 80 hours to recreate data.” — Sales Director, E-commerce Brand
Future Trends in CRM System Pricing
The CRM landscape is evolving. New pricing models, AI integration, and usage-based billing are reshaping CRM system pricing strategies.
Rise of Usage-Based and Outcome-Based Pricing
Traditional per-user pricing is being challenged by usage-based models. Instead of paying per seat, you pay based on activity—emails sent, leads processed, or API calls made.
For example, some emerging CRMs charge $0.01 per lead processed. This benefits businesses with fluctuating workloads. Outcome-based pricing—where you pay a percentage of revenue generated—is also gaining traction, though still rare.
- Reduces waste during low-activity periods
- Aligns vendor success with customer success
- Harder to predict long-term costs
Expect more vendors to experiment with these models by 2025.
AI and Automation: Premium Features or Standard?
AI-powered features like lead scoring, chatbots, and predictive analytics were once premium add-ons. Now, platforms like Zoho and HubSpot include basic AI in mid-tier plans.
However, advanced AI (e.g., Salesforce Einstein GPT) remains expensive. Expect AI to become standard in entry-level CRMs within 3–5 years, but high-end AI will stay behind paywalls.
“AI will reduce manual data entry by 70%, but only if you can afford the $100/user/month plan.” — Gartner, 2023
Consolidation and Bundled Suites
CRM vendors are bundling more tools into single platforms. HubSpot offers CRM, marketing, sales, service, CMS, and operations in one suite. Salesforce has Sales, Service, Marketing, Commerce, and Experience Clouds.
Bundling can reduce costs and improve integration, but may force you to pay for unused tools. Evaluate whether you need the full suite or just the CRM module.
Tip: Some vendors offer à la carte pricing—choose only what you need.
Strategies to Reduce CRM System Pricing Costs
You don’t have to overpay for a powerful CRM. Smart strategies can significantly reduce CRM system pricing without sacrificing functionality.
Start Small and Scale Gradually
Begin with the lowest viable plan and upgrade as needed. Many businesses over-provision at the start, paying for features they won’t use for months.
- Start with free or starter plans
- Add automation and reporting only when necessary
- Scale user licenses as your team grows
This approach improves ROI and allows your team to adapt gradually.
Bundle Services and Negotiate Enterprise Contracts
If you’re a mid-sized or large business, negotiate bundled pricing across multiple products (e.g., CRM + marketing automation + telephony).
- Ask for multi-year discounts
- Request free training or implementation
- Bundle with other software (e.g., Microsoft 365, Google Workspace)
Vendors like Salesforce and Microsoft offer enterprise agreements with significant savings.
Leverage Open Source and Community Editions
For tech-savvy teams, open-source CRMs like SuiteCRM or EspoCRM offer full control at low cost. While they lack vendor support, they eliminate subscription fees entirely.
- No recurring licensing costs
- Full customization freedom
- Requires in-house IT or developer support
Best for organizations with development resources and data privacy concerns.
What is the average cost of a CRM system?
The average cost of a CRM system ranges from $12 to $300 per user per month. Small businesses typically spend $50–$200/month, while enterprises can pay tens of thousands annually. Additional costs for implementation, training, and integration can double the total expense.
Is there a truly free CRM with no hidden costs?
While platforms like HubSpot and Zoho offer free CRM tiers, they often include limitations like branding, user caps, or restricted features. Truly ‘free’ CRMs with no hidden costs are rare—most aim to upsell you to paid plans.
Can I negotiate CRM pricing with vendors?
Yes, CRM pricing is often negotiable, especially for annual payments, multi-year contracts, or enterprise deals. Vendors may offer discounts, free training, or waived setup fees to close the deal.
Which CRM offers the best value for small businesses?
Zoho CRM and HubSpot are widely regarded as the best value for small businesses. Zoho offers robust features at low prices, while HubSpot provides a powerful free tier and seamless scalability.
How do I calculate the total cost of a CRM?
To calculate total CRM cost, add subscription fees, implementation, training, integration, customization, and renewal increases over 3–5 years. Use this formula: (Monthly Fee × 12 × Users) + Implementation + Training + Annual Support + Integration Costs.
Choosing the right CRM system pricing model requires balancing upfront costs with long-term value. From understanding deployment models to avoiding hidden fees, the key is to evaluate your real needs, calculate total ownership costs, and negotiate wisely. Whether you opt for a free starter plan or an enterprise suite, the goal is to maximize ROI while minimizing waste. The future of CRM pricing is shifting toward flexibility and value-based models, so stay informed and adaptable. Your CRM should empower your team—not drain your budget.
CRM system pricing – CRM system pricing menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Further Reading: